Leave A Message: info@paramparafertility.com
URODYNAMICS STUDY
Urinary incontinence is the involuntary leakage of urine. Types
1. Urge incontinence: You have a sudden, intense urge to urinate followed by an involuntary loss of urine.
Treatment
1. Bladder Retraining
2. Pelvic Floor Muscle Training
3. Lifestyle Changes
4. Dietary modification
It also may help to stop eating foods that may irritate the bladder such as Caffeine, Highly acidic foods such as citrus fruits and juices, Spicy food, artificial sweeteners.
Medications: Antibiotics, Anticholinergics, Cranberry medication etc.,
2. Stress Incontinence is the loss of urine during physical activity with cough, laugh, sneeze, bending, jumping..etc.,
Treatment
Behavioral Therapy
Pelvic Floor Muscle Training
Medications
Surgical Treatment: TVT-O sling, TVT sling, PUBO Vaginal sling, BURCH through Abdominal or Laparoscopic.
3. Overflow Incontinence: is a form of urinary incontinence, characterized by the involuntary release of urine from an overfull urinary bladder.
Treatment
Behavioral therapy: Time Voiding, Reduce Fluid intake Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises
Medications: control of Diabetes, Neurogenic problems, Bladder medications. Self Catheterization
4. Pelvic organ prolapse: refers to the prolapse or drooping of any of the pelvic floor organs, including:
1. Bladder
2. Uterus
3. Vagina
4. Small bowel
5. Rectum.
Treatment
Stage 1 to 2: Mild
1.Life style changes
2. Weight reduction
3. Pelvic floor muscle exercises
4. Vaginal Pessary ( ring)
Stage 3: Moderate to Severe
Surgical Treatment includes with or without vaginal Hysterectomy + Prolapse repair
1.Cystocele Repair
2.Vaginal Hysterectomy
3.Rectocele Repair
4.Sacrospinous fixation( Vaginally)
5.Sacrocolpo pexy through Open/ Laparoscopic/ Robotic
6.Paravaginal Defect repair through Open/ Laparoscopic/ Robotic
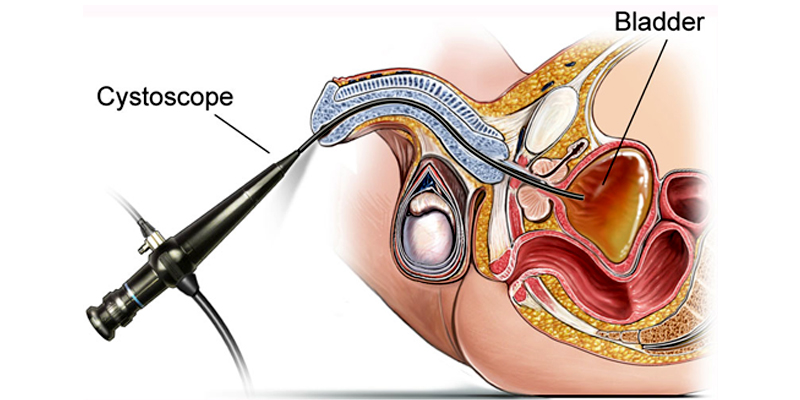
CYSTOSCOPE
A Cystoscope is a thin tube with a camera and light on the end. Cystoscopy is a test that allows look at the inside of bladder and urethra. This test done to diagnose urinary problems, such as a constant need to urinate or if the urination painful and to investigate reasons for blood in urine, frequent urinary tract infections, an overactive bladder, or pelvic pain.

PROGRESSION TO EXERCISE
- When sitting, standing or laying down, tighten the muscles around the back passage firmly, and then relax.
- Imagine you are stopping the flow of urine, by tightening the muscles around the front passage, and the relax.
- Tighten all the pelvic floor muscles by tightening first the anus then the front passage. Hold all together, and then relax
- As an advanced exercise, tighten the muscles around the front/back passage and while holding do a small cough, then release . Do this in sit to stand position, as this is when the pressure is greatest.
Do’s & Don’ts
- Do your pelvic floor exercises daily – you can do them anywhere, without anyone noticing-driving, watching TV, or waiting for the bus.
- Assess-how long you can hold a contraction ? 2 – 5 – 8 seconds
- Assess-how many times can you contract before you fatigue ? 4 – 6-8 repetitions
- Aim to increase both the time of contraction and the number of contractions
- Drink adequate amount of fluid a day
- Avoid becoming constipated
- Avoid going ‘just-in-case’. More than 8 times in 24 hours is too much
- Avoid Heavy lifting – repeated
- Avoid strenuous tummy exercise
- Do not hold your breath
- Do not push down. Squeeze your muscles together tightly and imagine that you are trying to lift this muscle up
- Do not tighten the muscles in your stomach, buttocks, or thighs
- Relax your pelvic floor muscles between each squeeze
- Plan for Doing Your Kegel Exercises
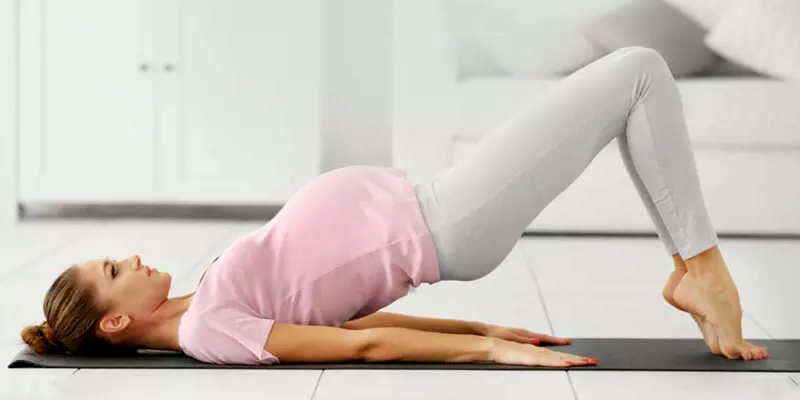

PELVIC FLOOR / KEGEL EXERCISE
In order to help strengthen your pelvic floor muscles, it is important that you take time to make sure you are exercising the right muscles. Try to stop and start your urine stream while you stand at your toilet. The muscles you use to stop your urine flow are your pelvic floor musclesEXERCISE
Position – Relaxed – High sitting
Holding the pelvic floor muscles for 5 seconds & relaxing Quick Contraction of the pelvic floor muscles
Position – Supine Position
Holding the pelvic floor muscles for 5 seconds & relaxing Quick Contraction of the pelvic floor muscles
Position – Supine position with both knees bent
Holding the pelvic floor muscles for 5 seconds & relaxing Quick Contraction of the pelvic floor muslces
Position – Supine Position with Both Knees bent
Hold the pelvic floor muscles, lifting the pelvis, holding 5 seconds, lowering the pelvis & relax the pelvic floor muscles
Position – Long sitting with both palms placed on the sides (floor)
Hold the Pelvic floor muscles, lifting the pelvis, holding for 5 seconds, lowering the pelvis & relax the pelvic floor muscles
Position – Quadruped Position
Holding the pelvic floor muscles for 5 seconds & relaxing
Treatments we done
Our Happy Patients
Talented Employees
Branches We Have